In today’s rapidly evolving world, traditional education models are struggling to keep pace with the demands of the 21st century. The integration of STEAM Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics into classrooms is not just a trend but a transformative approach to modern education. This interdisciplinary framework fosters critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills, preparing students for a future driven by innovation.
A Paradigm Shift in Education
The shift from rote learning to hands-on, inquiry-based education has become imperative in a world shaped by technology and global challenges. STEAM classrooms embody this shift, bridging theoretical knowledge with practical applications. Unlike traditional methods that often compartmentalize subjects, STEAM emphasizes interconnected learning. For example, a project on sustainable architecture might combine principles of physics, design, and environmental science, enabling students to see the real-world implications of their learning.
Why STEAM is the Future
- Encouraging Interdisciplinary Learning
- STEAM merges disciplines, showing students how they interact in real-world contexts. For instance, coding (technology) can be paired with storytelling (arts) to create interactive digital experiences, demonstrating the synergy between technical and creative fields.
- Fostering Innovation and Creativity
Incorporating the arts into STEAM broadens its scope, surpassing STEM’s emphasis on purely technical abilities. Creativity becomes a crucial element, encouraging students to think outside the box. This is particularly important in industries like product design, entertainment, and even healthcare, where innovation thrives at the intersection of technical expertise and artistic vision.
- Building Problem-Solving Skills
In a STEAM classroom, students tackle open-ended problems requiring holistic thinking. This process develops resilience and adaptability, essential traits for navigating an unpredictable future.
Real-World Applications of STEAM Education
- Robotics and AI Development
Students learn to design, build, and program robots while considering ethical implications, blending technology with critical thinking.
- Environmental Conservation Projects
Through STEAM, learners can analyze data, develop solutions for climate change, and create awareness campaigns, combining science, technology, and the arts.
- Game Design and Virtual Reality
Creating educational or entertainment games involves coding, storytelling, and visual arts, highlighting the interconnected nature of STEAM disciplines.
The Role of Technology in STEAM Classrooms
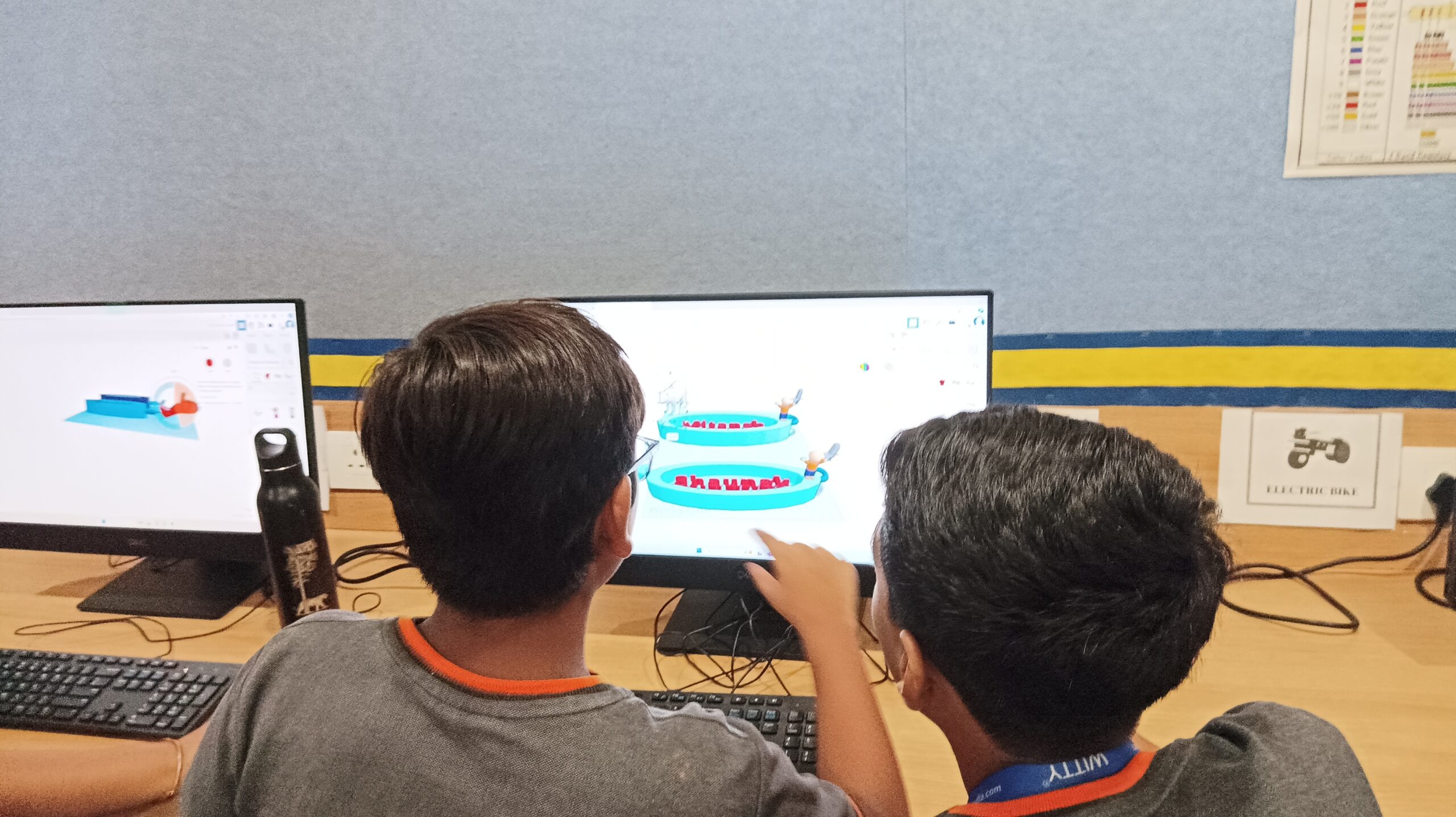
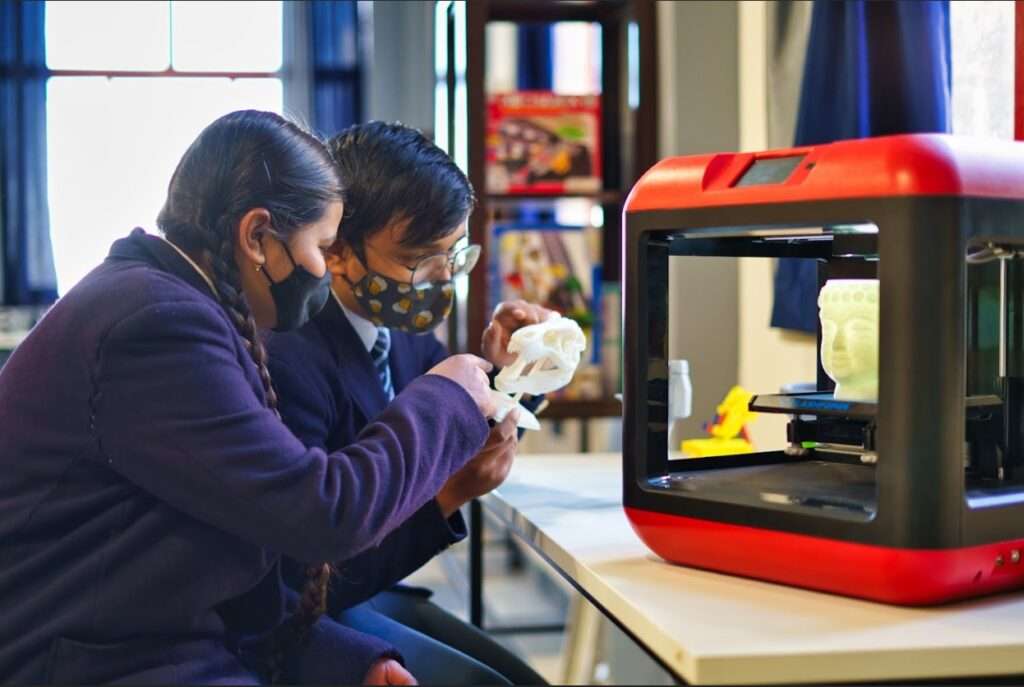
Technology acts as the backbone of STEAM education. Tools like 3D printers, coding platforms, and augmented reality make abstract concepts tangible. For example, a biology lesson on human anatomy can become more engaging through virtual reality simulations, enabling students to “travel” inside the human body.
STEAM and Modern Educational Goals
- Preparing Students for the Workforce
As automation and AI reshape industries, STEAM equips students with the skills required for emerging fields like data science, renewable energy, and digital marketing.
- Promoting Equity in Education
STEAM programs can bridge educational gaps by making learning engaging and accessible for diverse learners. Initiatives like coding bootcamps and maker spaces empower underprivileged students to explore opportunities in tech-driven careers.
- Enhancing Collaboration Skills
Group projects in STEAM classrooms simulate workplace environments, teaching students to collaborate, communicate, and respect diverse perspectives.
Challenges in Implementing STEAM Education
- Resource Constraints
Many schools lack access to advanced technology or trained educators. Bridging this gap requires investments in teacher training and infrastructure.
- Curriculum Integration
Traditional curriculums often resist change, making it challenging to incorporate STEAM. For seamless implementation, cooperation among policymakers, educators, and industry leaders is crucial.
- Assessment Models
Traditional assessment methods often fail to measure the diverse skills nurtured in STEAM classrooms. New metrics focusing on creativity, critical thinking, and innovation are needed.
Success Stories from STEAM Classrooms
In the United States, initiatives like the FabLab Program provide students with access to cutting-edge tools like laser cutters and 3D printers. Similarly, India’s Atal Tinkering Labs encourage young innovators to tackle real-world problems using STEAM principles. These programs have resulted in inventions ranging from water conservation systems to low-cost medical devices, showcasing the transformative potential of STEAM.
The Way Forward
To unlock the full potential of STEAM education, stakeholders must embrace collaboration. Governments should fund STEAM initiatives, while private sectors can offer mentorship programs and internships. Parents and communities also play a role in encouraging a growth mindset, where failure is viewed as a stepping stone to success.
Ready to bring STEAM to your classroom?
STEAM classrooms are not just about imparting knowledge; they are about nurturing a mindset ready to innovate, adapt, and excel in an ever-changing world. By breaking down silos between disciplines, STEAM prepares students to be the thinkers, creators, and leaders of tomorrow. Whether designing solutions for global challenges or advancing everyday conveniences, STEAM education is undeniably the cornerstone of modern educational innovation.
Explore resources, tools, and programs designed to transform learning experiences and inspire the next generation of innovators. Click here to get started!