A Classroom Where Subjects Connect
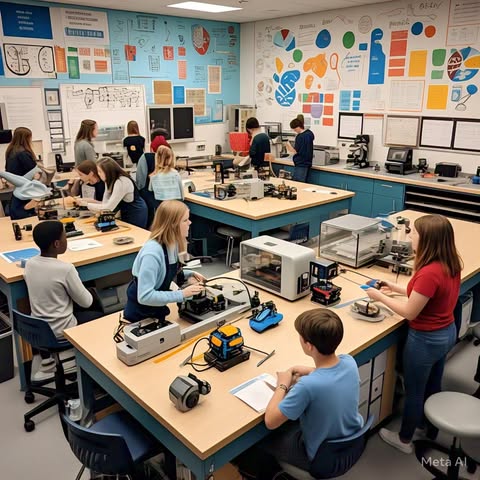
Ms. Patel, a high school teacher, noticed something fascinating in her STEM lab. Instead of students working on isolated math, science, or engineering lessons, they were designing water filtration systems, combining chemistry, physics, and environmental science. They weren’t just memorizing formulas—they were solving real-world problems.
This is the power of interdisciplinary learning, and STEM labs are the key. When students see how subjects connect, they develop a deeper understanding, think critically, and become better problem solvers. But how exactly does a STEM lab promote interdisciplinary education, and how can schools implement one effectively? Let’s dive in!
Why STEM Labs Are the Future of Interdisciplinary Learning
1. Blending Science, Math, and Technology for Real-World Applications
STEM labs eliminate the traditional boundaries between subjects. Instead of teaching math and science separately, students apply algebra in coding projects or physics in engineering prototypes.
Fact: The National Academy of Sciences found that students who learn through interdisciplinary STEM methods score 15% higher in problem-solving tests.
Example:
- A robotics project requires students to apply physics (motion and forces), coding (programming sensors), and math (calculating speed and distance).
- Chemistry students use data analysis to determine the effectiveness of different soil compositions for growing crops.
Why it works:
Students grasp concepts better when they see their real-world relevance.
Problem-solving skills improve as they learn to integrate multiple disciplines.
They develop adaptability, a crucial skill in today’s job market.
2. Enhancing Critical Thinking Through Hands-On Learning
Traditional learning often involves memorization, but STEM labs encourage exploration. When students work on interdisciplinary projects, they analyze, test hypotheses, and iterate their designs.
Fact: A study by the National Science Foundation (NSF) found that hands-on STEM activities improve student engagement by 32%.
Example:
- A project designing earthquake-resistant buildings combines engineering (structure design), physics (seismic waves), and computer simulations (data modeling).
Why it works:
Encourages students to think critically rather than just recall facts.
Fosters creativity and innovation through experimentation.
Builds resilience as students refine and improve their projects.
3. Preparing Students for Future Careers
The workforce is no longer divided into rigid fields. Today’s industries demand professionals who can merge skills from multiple disciplines—think biomedical engineers, AI-powered financial analysts, and data-driven environmental scientists.
Fact: The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 10.8% growth in STEM jobs by 2032, twice the rate of non-STEM fields.
Example:
- A biotech student designs a wearable health-monitoring device, applying biology, engineering, and AI-driven analytics.
Why it works:
Encourages students to explore emerging careers.
Prepares them for interdisciplinary roles in AI, healthcare, and engineering.
Builds the adaptability needed in a rapidly changing job market.
4. Fostering Collaboration and Teamwork
In STEM labs, students work in teams, solving complex challenges that require diverse skills. This mirrors real-world work environments, where professionals collaborate across departments.
Fact: Research by Harvard University shows that teamwork-based learning improves student performance by 25% compared to individual tasks.
Example:
- A team designing an eco-friendly smart home integrates mechanical engineering (energy efficiency), environmental science (sustainable materials), and coding (smart automation).
Why it works:
Strengthens communication and teamwork skills.
Encourages leadership and project management abilities.
Mimics real-world work settings, enhancing employability.
How to Implement a STEM Lab in Your School
Secure STEM Grants: Apply for funding from organizations like the National Science Foundation (NSF) or NASA Education Grants.
Partner with Tech Companies: Google, Microsoft, and Intel offer free software and mentorship programs.
Use Affordable STEM Kits: Start with budget-friendly tools like Raspberry Pi (coding), LEGO Mindstorms (robotics), and 3D printers for design projects
.
Train Teachers in STEM Education: Platforms like Coursera, Code.org, and MIT OpenCourseWare offer specialized STEM training.
Ready to Unlock Interdisciplinary Learning?
A STEM lab isn’t just a classroom upgrade—it’s a game-changer for student engagement, problem-solving, and future career readiness. Schools that invest in STEM labs see higher academic performance and better-prepared graduates.
Don’t wait start building a STEM lab in your school today!
Contact Maker Muse Today!
Website: https://makersmuse.in/
Email: info@makersmuse.in