The Future of Drones for Kids Education Takes Flight
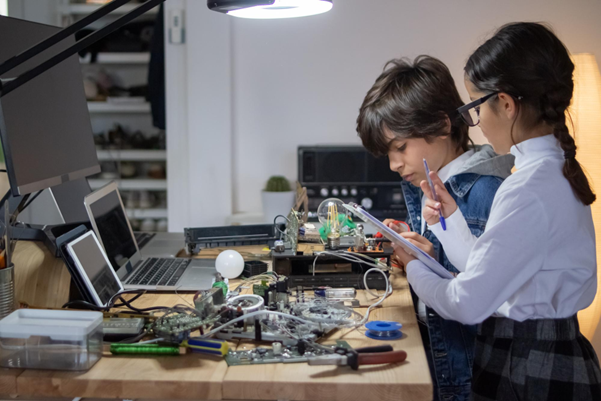
Picture this: students gathering around a 3D printer, watching their custom drone frame take shape layer by layer. Within hours, they’ll program their creation to navigate obstacle courses, collect data, and solve real-world problems. This isn’t science fiction—it’s happening in forward-thinking schools worldwide.
What is a drone? Simply put, it’s an unmanned aerial vehicle that opens doors to countless learning opportunities. But for educators, drones represent something far more valuable: a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application that transforms how students engage with science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
The educational drone market is experiencing unprecedented growth. Drones are boosting hands-on STEM and vocational learning, enhancing student engagement and workforce skills, making them essential tools for modern education. Schools that embrace this technology today are preparing students for tomorrow’s careers.
This comprehensive guide explores everything educators need to know about implementing drone programs, from understanding basic mechanics to advanced 3D printing projects. Whether you’re a teacher, administrator, or curriculum developer, you’ll discover how drones can revolutionise your classroom experience.

Why Learning Drone Technology Matters for Students
Building Future-Ready Skills
The question isn’t whether students should learn about drones—it’s how quickly schools can implement effective programs. Working with drones can motivate students, as well as teach skills like coding, collaboration, and problem-solving. These aren’t just technical skills; they’re the foundation of 21st-century learning.
When students learn how drones work, they’re mastering:
- Physics concepts: Lift, thrust, aerodynamics, and energy transfer
- Programming skills: Coding flight paths and autonomous behaviours
- Problem-solving: Troubleshooting technical issues and design challenges
- Teamwork: Collaborating on complex projects and sharing responsibilities
- Creative thinking: Designing unique solutions and applications
Real-World Applications
Modern drones serve countless industries, from precision agriculture to emergency response. Students who understand drone technology gain insight into career paths they might never have considered. Agricultural drones monitor crop health, construction drones survey building sites, and rescue drones locate missing persons—all applications that demonstrate technology’s positive impact on society.
Understanding How Drones Work
The Physics Behind Flight
How do drones work? The answer lies in understanding four fundamental forces: lift, weight, thrust, and drag. Unlike aeroplanes that generate lift through forward motion, drones create lift through rapidly spinning rotors that push air downward.
Each rotor speed can be adjusted independently, allowing precise control over altitude, movement, and rotation. The flight controller—the drone’s “brain”—processes sensor data and adjusts rotor speeds hundreds of times per second.
Electronic Components Explained
Modern educational drones integrate multiple sophisticated systems:
Flight Controller: Processes sensor data and maintains stable flight.
Sensors: Gyroscopes detect orientation, and accelerometers measure movement.
Motors and Propellers: Brushless motors provide efficient power.
Battery Systems: Lithium polymer batteries deliver high power density
How Kids Can Learn Through Structured Programs
Progressive Curriculum Development
Effective drone education follows a structured approach that builds knowledge systematically:
Foundation Level (Ages 8-10): Basic operation, safety, and simple programming concepts. Intermediate Level (Ages 11-13): Building from kits, programming autonomous behaviour.s Advanced Level (Ages 14+): Custom design, 3D printing, and real-world problem-solving
Hands-On Learning Approaches
The most effective drone programs emphasise experiential learning. Students don’t just study concepts—they experience them firsthand through project-based learning, collaborative teams, and friendly competitions that motivate while teaching perseverance.

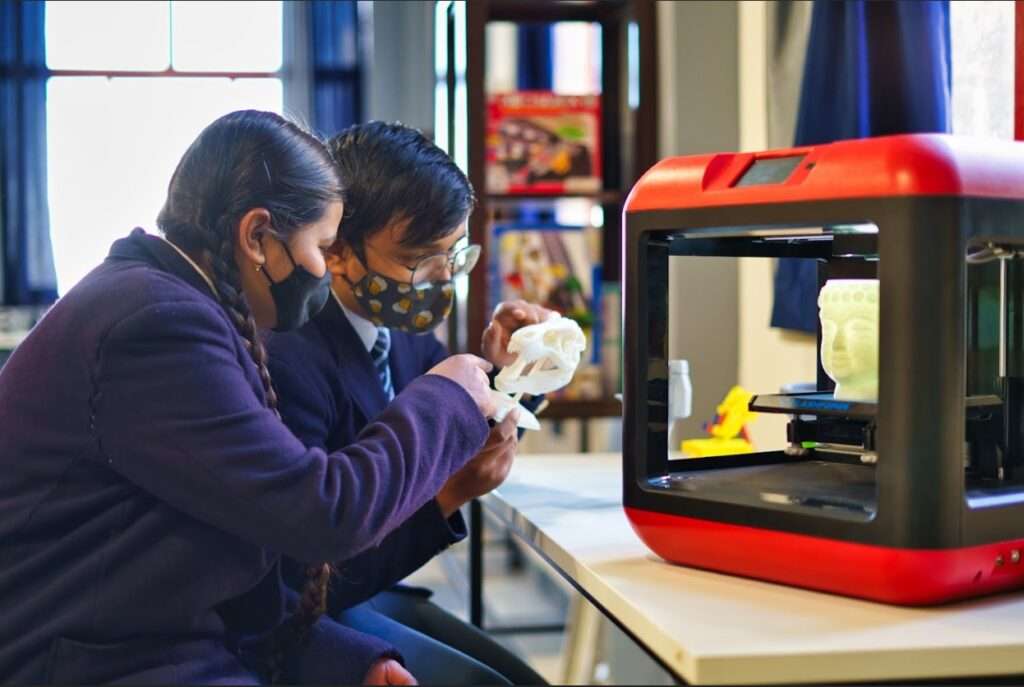
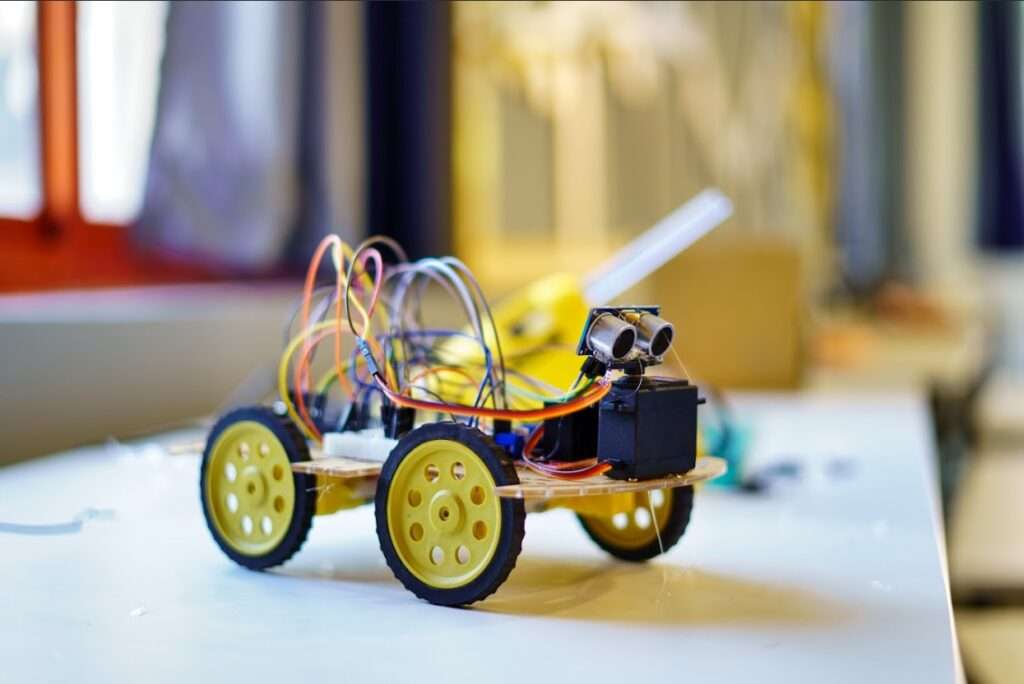
3D-Printed Drones: Innovation in Action
The Power of Custom Design
3D-printed drones represent the perfect intersection of manufacturing technology and aerospace engineering. With 3D printing, we were able to save 40% of time in the product design and development process. The total weight of the drone was also reduced by a factor of 20%.
Students can design custom frames optimised for specific missions, create replacement parts instantly, and experiment with different materials and designs. This hands-on approach makes engineering principles tangible rather than abstract.
Educational Benefits
3D-printed drones offer unique learning opportunities in design thinking, engineering principles, and manufacturing skills. Students learn to identify problems, brainstorm solutions, prototype rapidly, and iterate based on testing results.
Essential Materials and Tools
Basic Equipment List
Starting a drone program requires careful planning and appropriate equipment:
For 3D Printing: 3D printer (FDM or resin), PLA or PETG filament, design software (Fusion 360, Tinkercad), safety equipment
For Drone Assembly: Screwdrivers and hex keys, soldering equipment, multimeter for testing, hot glue gun for quick fixes
For Programming: Computers or tablets, programming software, USB cables and adapters, backup batteries and chargers
Budget Considerations
Schools can start drone programs with modest budgets by beginning with pre-built educational drones, gradually adding 3D printing capabilities, partnering with local makerspaces, and applying for STEM education grants.
Building Your First Drone: A Step-by-Step Guide
Planning and Design
Before building begins, students should define their drone’s purpose, research existing designs, create detailed plans, and consider safety requirements.
Assembly Process
Frame Construction: Whether 3D-printed or purchased, the frame must be lightweight yet durable. Students learn about material properties and structural engineering.
Electronics Integration: Connecting flight controllers, sensors, and batteries teaches circuit design and electrical safety while introducing embedded systems concepts.
Testing and Refinement
Initial flights rarely go perfectly, providing excellent learning opportunities. Students learn to identify problems through systematic testing, develop solutions, and document improvements.
Critical Safety Considerations
Establishing Safety Protocols
Safety must be the foundation of any drone program. For a child’s drone, the first landing site is the room, so pay attention to mini and micro models. Schools should implement comprehensive safety protocols covering physical safety, operational procedures, and emergency responses.
Physical Safety: Designated flight areas, protective equipment, emergency procedures, and regular equipment inspections
Operational Safety: Pre-flight checklists, weather considerations, battery safety protocols, and proper storage procedures
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Educational drone programs must comply with local regulations, including registration requirements, operator certification, airspace restrictions, and privacy considerations.
The Future of Drones in Education
Emerging Trends
The educational drone landscape continues to evolve rapidly. The drone industry in 2024 is marked by technological advancements such as enhanced battery life, sophisticated sensors, and improved safety features. Schools implementing programs now will be positioned to take advantage of these improvements.
Preparing for Tomorrow
As drone technology advances, educational programs must evolve accordingly. 5G technology will play a pivotal role, enabling seamless connectivity for drones, unlocking new possibilities for real-time communication and complex operations.
Students today are learning skills that will serve them throughout their careers, regardless of how technology changes. The critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills developed through drone programs transfer to countless future opportunities.

Conclusion: Taking Flight with Confidence
Drones for kids represent more than just an engaging classroom tool—they’re a gateway to comprehensive STEM education that prepares students for an increasingly technological world. From understanding basic physics to designing custom 3D-printed frames, students gain hands-on experience that makes abstract concepts tangible and exciting.
The benefits extend far beyond technical knowledge. Students develop confidence, creativity, and collaboration skills while exploring potential career paths they may have never considered. Schools that implement thoughtful drone programs create learning environments where students don’t just study technology—they become creators and innovators.
Success requires careful planning, appropriate safety measures, and ongoing support for both students and educators. But the investment pays dividends in student engagement, skill development, and future readiness.
As we look to the future, drone technology will continue to evolve, creating new opportunities and challenges. Schools that embrace this technology today are positioning their students for success in tomorrow’s workforce while making learning more engaging and relevant than ever before.
The question isn’t whether your school should implement a drone program—it’s how quickly you can get started. With proper planning, appropriate resources, and a commitment to safety and excellence, your students can begin their journey into the exciting world of drone technology.
Ready to launch your school’s drone program and watch your students soar to new heights? Book your free trial class today and discover how drone technology can transform your STEM education experience!